Note, I’ve turned off (see eval=FALSE) in python code chunks below in case you have not installed python.
Slide 35
In R, load libraries,
library(tidyverse)or in Python do the same,
import pandas as pd
from plotnine import *
from siuba.dply.vector import row_number, n, lag
from siuba import *Slide 36
In R, import data from Citi Bike data storage if not available on your computer:
savefile <- "data/201901-citibike-tripdata.csv"
if (!file.exists(savefile)) {
url <- str_c(
"https://s3.amazonaws.com/tripdata/",
"201901-citibike-tripdata.csv.zip"
)
download.file(url = url, destfile = savefile )
}
df_r <- read_csv(savefile)Let’s look at the beginning of the dataframe:
df_r %>% glimpse() Rows: 967,287
Columns: 15
$ tripduration <dbl> 320, 316, 591, 2719, 303, 535, 280…
$ starttime <dttm> 2019-01-01 00:01:47, 2019-01-01 0…
$ stoptime <dttm> 2019-01-01 00:07:07, 2019-01-01 0…
$ `start station id` <dbl> 3160, 519, 3171, 504, 229, 3630, 3…
$ `start station name` <chr> "Central Park West & W 76 St", "Pe…
$ `start station latitude` <dbl> 40.77897, 40.75187, 40.78525, 40.7…
$ `start station longitude` <dbl> -73.97375, -73.97771, -73.97667, -…
$ `end station id` <dbl> 3283, 518, 3154, 3709, 503, 3529, …
$ `end station name` <chr> "W 89 St & Columbus Ave", "E 39 St…
$ `end station latitude` <dbl> 40.78822, 40.74780, 40.77314, 40.7…
$ `end station longitude` <dbl> -73.97042, -73.97344, -73.95856, -…
$ bikeid <dbl> 15839, 32723, 27451, 21579, 35379,…
$ usertype <chr> "Subscriber", "Subscriber", "Subsc…
$ `birth year` <dbl> 1971, 1964, 1987, 1990, 1979, 1989…
$ gender <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2…Of note, as of R 4.2, the base language includes a pipe operator |>, but I’ll continue to use %>% from the R package magrittr as it has more features.
In Python, load our data:
df_py = pd.read_csv("data/201901-citibike-tripdata.csv")As with R, let’s get some information on the data frame:
df_py.info()Slide 37
In R, let’s create a new variable that flags whether the bike was rebalanced.
df_r <- df_r %>% rename_all(function(x) str_replace_all(x, ' ', '_'))
df_r <- df_r %>%
filter(!is.na(start_station_id)) %>%
arrange(starttime) %>%
group_by(bikeid) %>%
mutate(
rebalanced = (row_number() > 1) & (start_station_id != lag(end_station_id))
) %>%
ungroup()
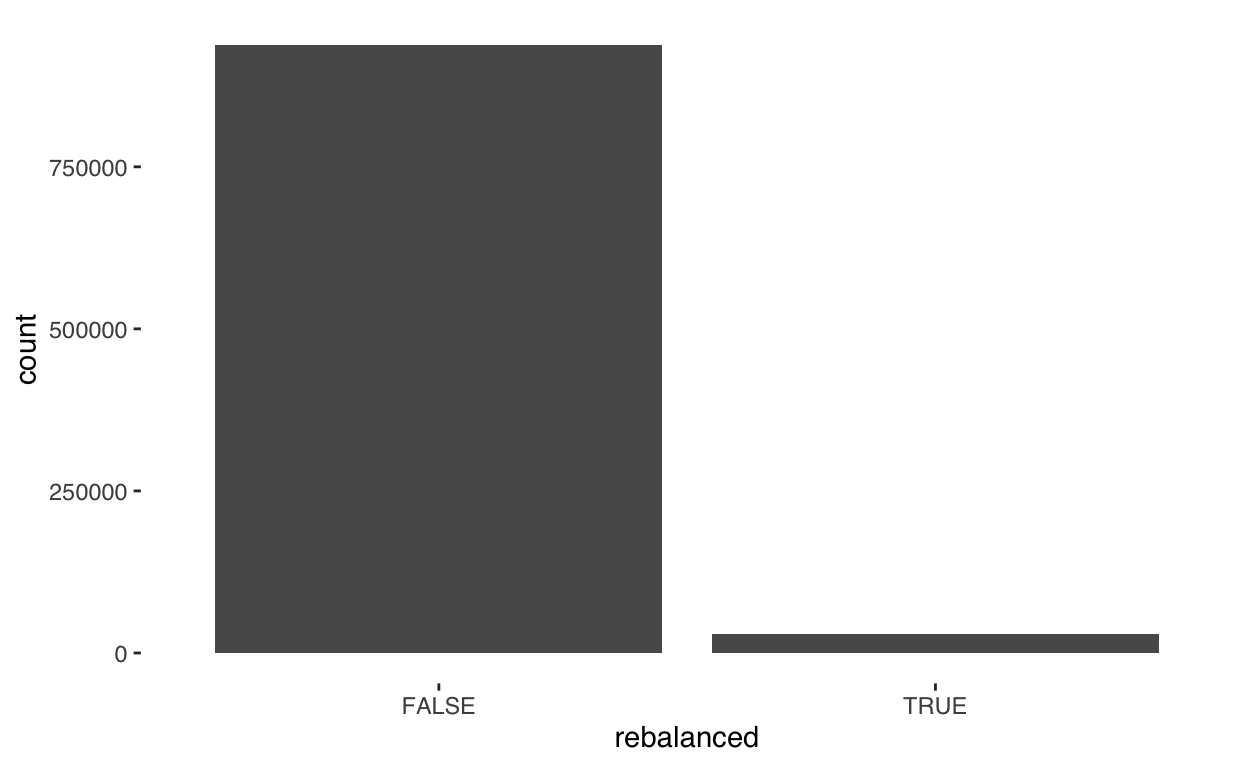
df_r %>% pull(rebalanced) %>% table().
FALSE TRUE
937908 29361 In Python,
df_py = df_py.rename(lambda x: x.replace(' ', '_'), axis = 1)
df_py = df_py >> \
filter( _.start_station_id.notnull() ) >> \
arrange( _.starttime ) >> \
group_by( _.bikeid ) >> \
mutate(
rebalanced = (row_number(_) > 1) & (_.start_station_id != _.end_station_id.shift(1) )
) >> \
ungroup()
df_py.rebalanced.value_counts( dropna = False )Slide 38
In R,
ggplot(data = df_r) +
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = rebalanced),
stat = 'count'
)
In Python,
ggplot(df_py) + \
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = 'rebalanced'),
stat = 'count'
)Slide 39
In R, we may code a simple linear regression using the base R function lm like so,
df_r <- df_r %>% mutate(gender_factor = factor(gender) )
model1 <- lm(
formula = tripduration ~ rebalanced + gender_factor,
data = df_r)
summary(model1)
Call:
lm(formula = tripduration ~ rebalanced + gender_factor, data = df_r)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1727 -443 -250 79 2678123
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 1717.67 38.69 44.401 <2e-16 ***
rebalancedTRUE 70.10 42.34 1.656 0.0978 .
gender_factor1 -1005.53 39.56 -25.418 <2e-16 ***
gender_factor2 -883.02 41.74 -21.153 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 7142 on 967265 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.0006904, Adjusted R-squared: 0.0006873
F-statistic: 222.7 on 3 and 967265 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16and a generalized linear model using the base R function glm:
model2 <- glm(
formula = rebalanced ~ tripduration + gender_factor,
data = df_r,
family = binomial())
summary(model2)
Call:
glm(formula = rebalanced ~ tripduration + gender_factor, family = binomial(),
data = df_r)
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) -3.459e+00 3.148e-02 -109.885 < 2e-16 ***
tripduration 7.722e-07 4.930e-07 1.566 0.1172
gender_factor1 -5.771e-02 3.224e-02 -1.790 0.0735 .
gender_factor2 1.610e-01 3.364e-02 4.787 1.69e-06 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
(Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 263044 on 967268 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 262799 on 967265 degrees of freedom
AIC: 262807
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 6In Python, we can calculate the same models using the statsmodels library. Here’s the linear model:
import statsmodels.api as sm
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
df_py = df_py >> mutate(gender_factor = _.gender.astype('category') )
model1 = smf.ols(
formula = 'tripduration ~ rebalanced + gender_factor',
data = df_py).fit()
model1.summary()and here’s the generalized linear model,
model2 = smf.glm(
formula = 'rebalanced ~ tripduration + gender_factor',
data = df_py,
family = sm.families.Binomial() ).fit()
model2.summary()